As electric mobility surges worldwide, the EV charging landscape is evolving fast — shifting from traditional power solutions to intelligent, sustainable, and energy-flexible systems. 🚗⚡

The latest trend combines smart charging with solar energy ☀️ and battery storage 🔋, creating cleaner, more resilient power networks that shape the future of green transportation.
🌱 Accelerating the Energy Transition
Traditional EV chargers often rely on complex grid connections and long installation timelines.
🌞⚡In contrast, smart charging systems with solar + storage integration can operate semi-independently from the grid — reducing peak loads, speeding up installation, and maximizing renewable power use.
These hybrid systems store solar energy during the day ☀️ and release it during high-demand hours 🌙, balancing the grid and cutting operational costs. 💰

🔋 Battery-Buffered Charging: A Smarter Path Forward
A new generation of battery-buffered ultra-rapid chargers is reshaping the market.
Instead of waiting 3–6 years for utility upgrades, these systems can be deployed in as little as 1–2 years. ⏱️
By integrating on-site energy storage, they deliver high-power, stable charging even in locations with limited grid capacity.
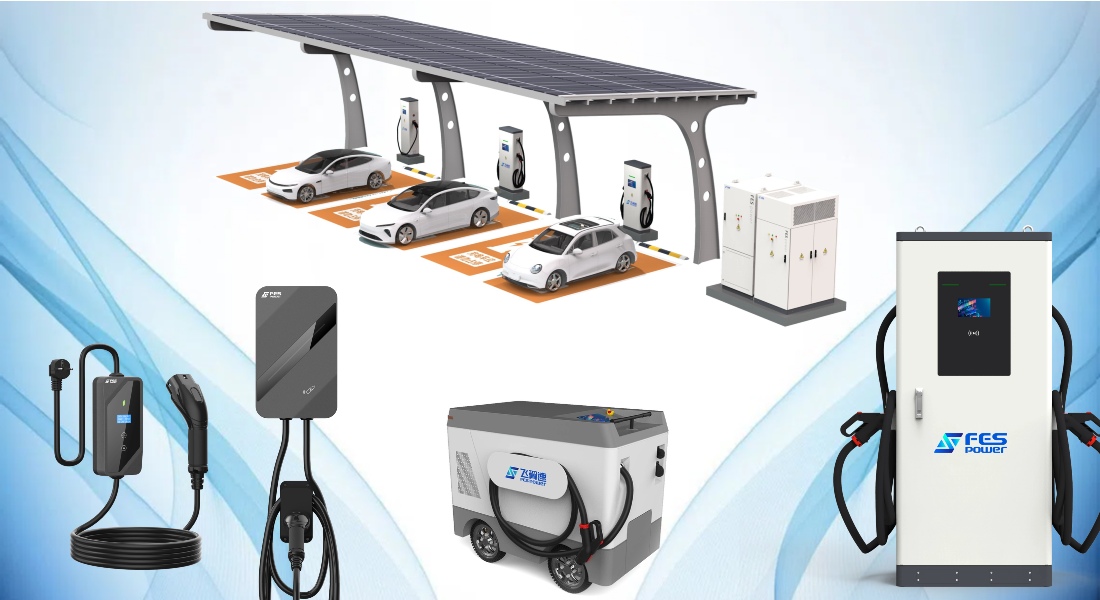
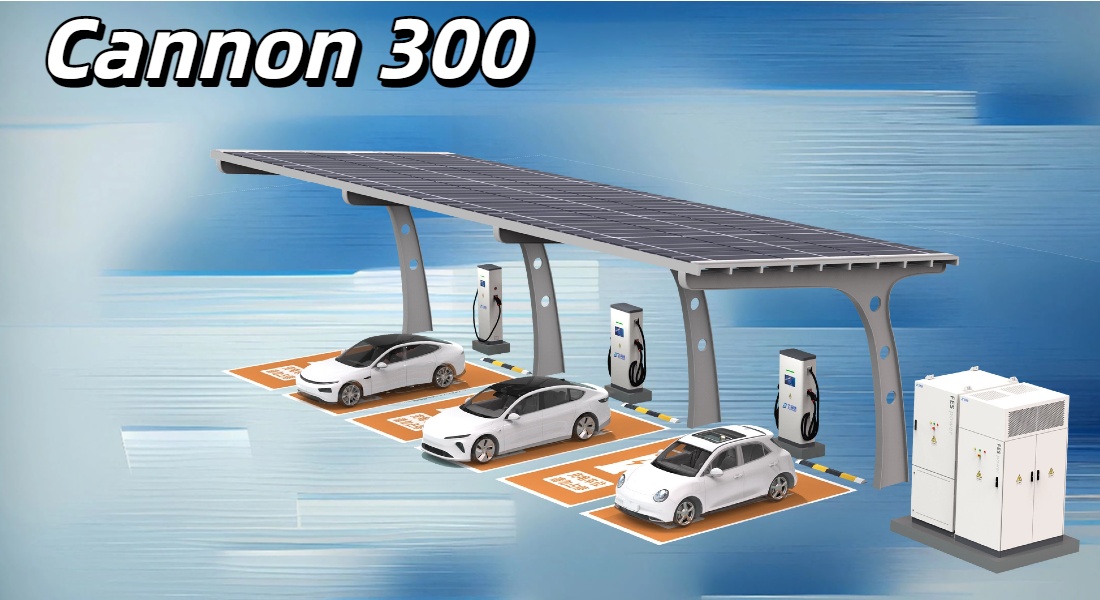
⚡ Cannon 300 — FES Power’s Answer to the Future
FES Power’s Cannon 300 redefines what “smart charging” means.
It combines ultra-rapid performance, renewable readiness, and modular scalability, making it ideal for modern EV hubs, fleets, and highway stations. 🏙️🚚
✨ Key Highlights:
🔌 Up to 600 kW ultra-fast output, supporting 600 A liquid-cooled and 250 A air-cooled dispensers.
🔋 Built-in LiFePO₄ battery (150–260 kWh) for flexible and stable energy use.
☀️ PV integration with MPPT function — directly utilizes solar power.
🌐 Smart communication: Ethernet, 4G/LTE, Wi-Fi, and OCPP 1.6J/2.0.
❄️ Operates from -25 °C to 55 °C, low noise (<45 dB Eco mode).
🧠 Works in grid-tied or off-grid mode for full deployment flexibility.
🌍 Building a Cleaner, Smarter Future

By integrating solar energy, storage systems, and smart control, Cannon 300 enables faster, cheaper, and greener charging infrastructure. 💡
It’s not just a charging station — it’s a complete energy ecosystem built for the new era of e-mobility. 🚘🌱
FES Power — Empowering the Future of Energy Transition